I feel like people that think they are smart in finance are really idiots. On sunday a guy that is a finacial advisor or some shit was talking about investments while I was golfing. I was like I'm good I just save all my money in BTC and it works for me.
He's like "Microstrategy is going to have to sell 2.5 billion in BTC to pay off the notes that they sold to buy bitcoin and that will have a drag on BTC price." I was like no dude it's all convertible notes. They won't have to pay anything on them. He looked at me confused. I'm like people can convert the note to stock for a pre agreed upon price if MSTR is over that price at expiry they sell 0 BTC. I could tell he didn't even know what I was talking about but he said they will have a real issue being over those strike prices. I was like ok. I doubt it because it is just the price of stock at the time off issuance x the % the notes pay out. But ok.
To be honest I didn't know the expires or strike prices. Looked it up today.
1. $650 Million Notes (2025)
Adjusted Conversion Price: Approximately $39.80 per share
Maturity Date: December 15, 2025
2. $1.05 Billion Notes (2027)
Adjusted Conversion Price: Approximately $143.25 per share
Maturity Date: February 15, 2027
3. $500 Million Notes (2028)
Adjusted Conversion Price: Approximately $158.19 per share
Maturity Date: February 15, 2028
4. $400 Million Notes (2029)
Adjusted Conversion Price: Approximately $123.60 per share
Maturity Date: December 15, 2029
The high today was $151.87. BTC got some work to do by feb 15 2029! 😆
Bitcoin. Is pumping. Come to my telegram channel for more details! 😆 🤣
Read, "when money dies" all these clowns since government money started do the same shit to try to save their blood money. Their solutions speed up their downfall.
Joe Kernen is such a toxic maxi 🤌😂
And Elizabeth Warren is a condescending, insufferable totalitarian masquerading as a “protector of the little guys.” https://v.nostr.build/gKJ8Ii39zvOz4ua2.mp4
Clowns. They solution as old as time for government corruption. Ask the Roman's! Lol leads to increased crime with black markets and higher prices paying the crime premium. Less availability to people that don't use the black market. Destroys supply chains then even if someone less retarded comes in and removes the price freezes you have to start from scratch because supply lines are F'd.
Fools.
You guys hate me but Chatty thinks I'm keul. 
Ocean doesn't have a huge hashpool but they consistently find blocks. Much more advantageous for anyone that isn't a big money miner. 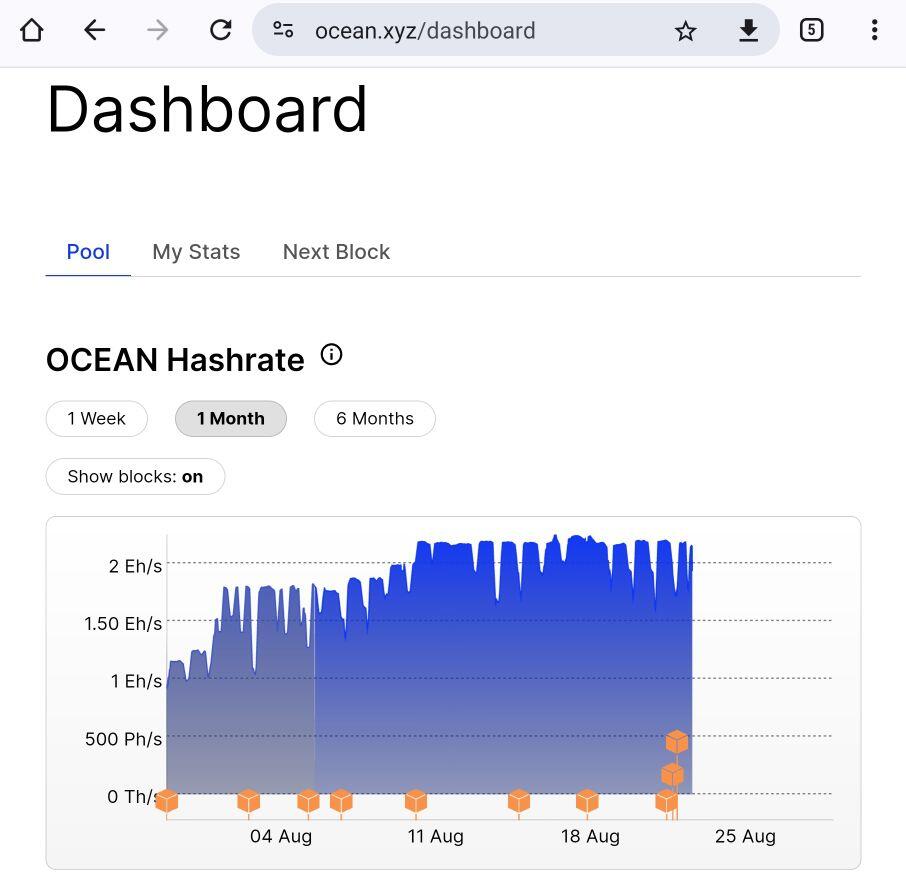
I think you will get pools like Ocean.xyz that take over in the coming years. You only need like half 1% of the hash to have consistent results. Then you should have a competition to run those and do what the independent miners want at the lowest fees.
Those big pools pay the big boys more than their hash share and are shady with fees and censorship. They just tie up miners. Of your bringing new hash online you'd be dumb to go to the bigs.
For you creeps that were wondering Laszlo got screwed on pizza day! 😆
BTC =$.0041 ouch.
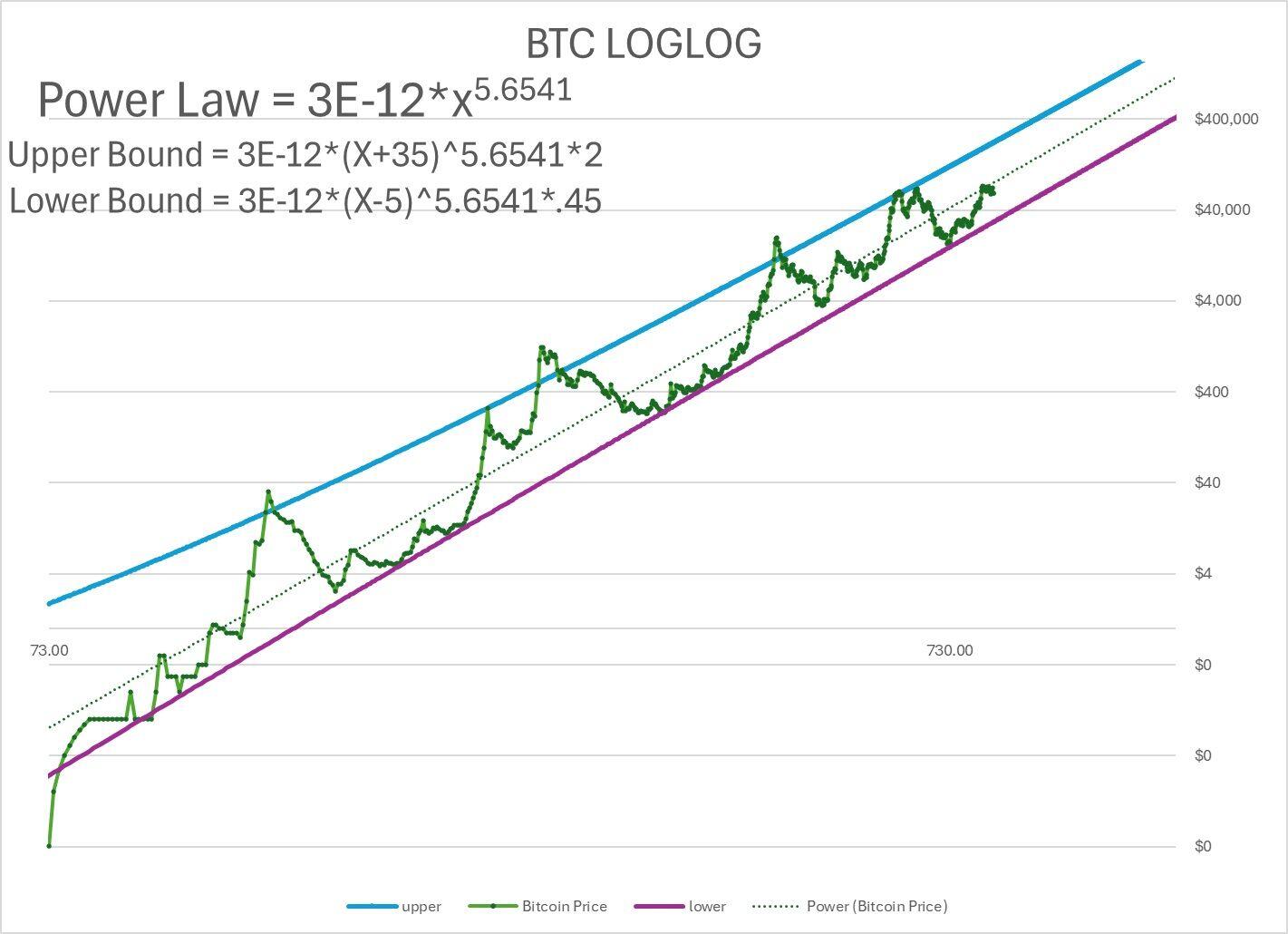
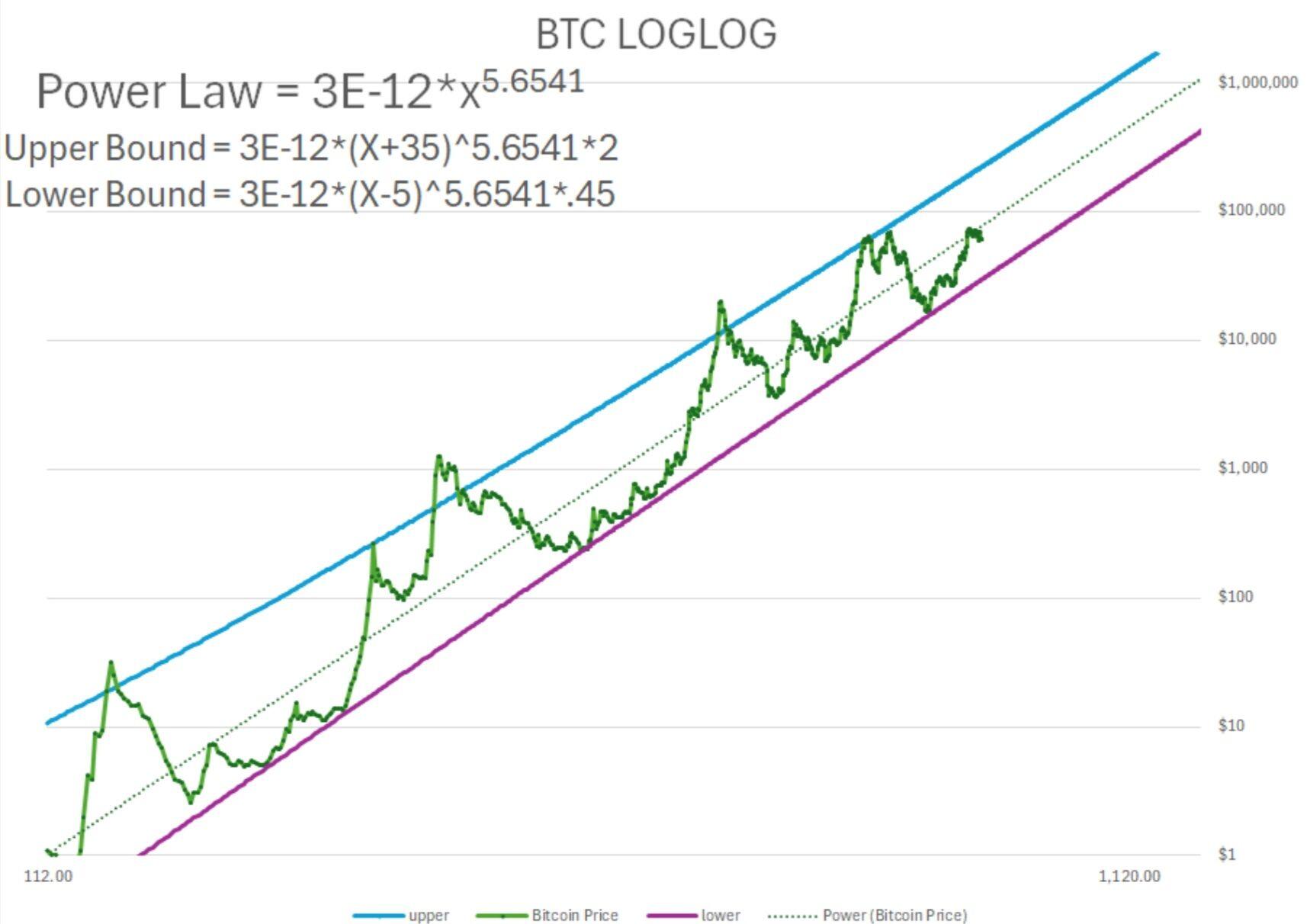
Downloaded every week's price since inception.
Took log log on price and time. Each week numerically #
Came up with loglog trend line used it to tweK upper and lower bounds.
If you want to use it x is week #
3 Jan 09 x=1
24 Aug 24 x=817 LB = 29,656. trend = 87,'724 UB = 222,408
Lower bound only broken 5 times all before 2015.
UB breaks $1mil August 18, 2029
Trend breaks $1mil January 29, 2033
LB breaks $1mil january 30, 2038
Thought this was pretty keul.
Being a weirdo and messing around with BTC old price points and S2F stuff and making log/log charts on excel. Log/Log 🤯🤯🤯🤯 by the way.
I know a lot of people hate stock to flow stuff but I think it is funny that S2F hit 1 on 3 Jan 2010 and Pizza day was only a few months later 22 May. USD of purchase was $41 Laszlo spent 10,000 BTC. Each BTC was $0.0041 or .41 of a penny. It actually fits pretty nicely on the log/log trend line!
Hivemind! 🐝🐝🐝🐝🐝🐝🐝🐝🐝
Of cyber hornets.
Free markets are kinda amazing.... we should try communism! 😆
The first significant increase in the federal income tax rates occurred during World War I. The U.S. government needed additional revenue to finance the war effort, leading to several changes in the tax system.
### Key Increases:
- **Revenue Act of 1916**: This act increased the basic tax rate from 1% to 2% on incomes over $3,000 for single filers and $4,000 for married couples. It also expanded the surtax brackets, with the highest rate reaching 15% on incomes over $2 million.
- **Revenue Act of 1917**: As the U.S. entered World War I, the need for revenue grew more urgent. This act further increased the basic rate to 2% and expanded the surtax rates. The surtax ranged from 1% on incomes over $5,000 to a maximum of 50% on incomes over $1 million.
- **Revenue Act of 1918**: This act was enacted towards the end of World War I and represented the most substantial increase during this period. The basic tax rate was raised to 6%, and the surtax rates were further expanded, with the highest rate reaching 77% on incomes over $1 million.
### Impact:
These increases reflected the government's need to fund the war and marked the beginning of a trend toward higher and more progressive income tax rates in the U.S., particularly during times of national crisis. The top marginal rates during this period were among the highest in U.S. history, and the income tax became a significant source of federal revenue.
To impose an income tax without apportioning it among the states, Congress proposed the 16th Amendment, which states:"The Congress shall have power to lay and collect taxes on incomes, from whatever source derived, without apportionment among the several States, and without regard to any census or enumeration."This amendment was ratified by the required number of states on February 3, 1913, and effectively gave Congress the clear constitutional authority to impose a federal income tax.
The first federal income tax in the United States, after the ratification of the 16th Amendment in 1913, primarily affected wealthier individuals. Here are the details:
### Who Was Affected:
- The tax applied only to individuals with higher incomes. Specifically, it was aimed at those earning more than $3,000 per year (equivalent to about $90,000 today when adjusted for inflation).
- For married couples, the threshold was $4,000 (approximately $120,000 today).
- Because the average income at that time was much lower, this tax affected a relatively small percentage of the population, estimated at less than 1% of Americans.
### Tax Rates:
- The income tax rates were initially very low:
- The basic rate was 1% on income above the threshold ($3,000 for individuals and $4,000 for couples).
- Additionally, there was a "surtax" for higher incomes. This surtax started at 1% for incomes over $20,000 and rose to 6% for incomes over $500,000.
### Revenue and Impact:
- The goal of the tax was to generate revenue for the federal government from the wealthiest citizens.
- It was designed to be progressive, meaning that the tax rate increased as income increased, placing a larger burden on the wealthy.
This income tax structure marked a significant shift in the way the federal government raised revenue, moving away from tariffs and excise taxes and towards income taxation, which would become the primary source of federal revenue in the years to come.
This is pure evil. This is for the "richest" people! This is exactly how they destroyed the constitution. It was unconstitutional to tax your income. But everyone supported getting ride of that constitutional right to tax the "richest" people so they could do their part.
Oooooops.
Chat gpt wants you to know. New ATH between October 10th and November 12th.
High of the post halvening run expected July 27 to Aug 25 2025
High of $271,000 to $281,000!!!!
Thank you, Chatty. I was in the mood for some bullish AFAI hopium!
LFG!!!


Never heard of it. Pretty interesting.
Gotta love South Park! 
Would you like to play a game?