May the stars carry your sadness away, may the flowers fill your heart with beauty, may hope forever wipe away your tears. And, above all, may silence make you strong.
#ChiefDanGeorge

#HaidaGwaii
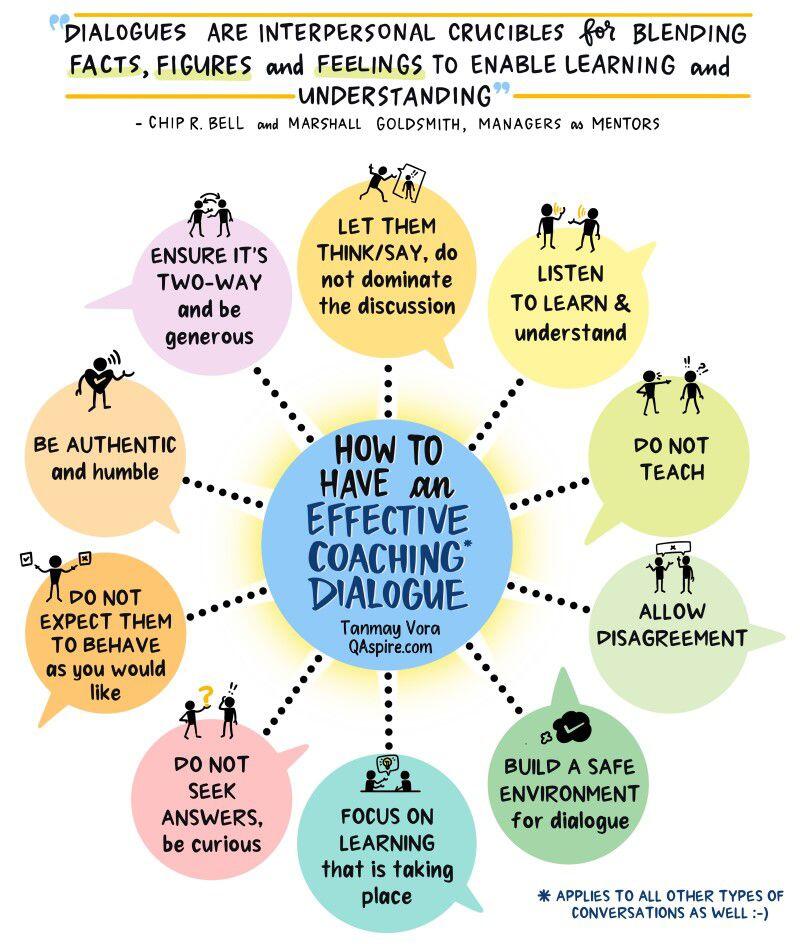
#TheArtOfThinking

#Criticalthinking skills are essential for navigating the complex and ever-changing world we live in.
They allow individuals to approach problems, questions, and situations with a thoughtful and analytical mindset.
Enabling them to make informed decisions and draw well-reasoned conclusions.
The development and application of critical thinking skills involve various cognitive processes, which can be categorized into six key components:
knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation.
Knowledge forms the foundation of critical thinking. It refers to the acquisition and understanding of information, facts, concepts, and principles relevant to a given topic or issue. Without a solid base of knowledge, individuals may struggle to engage in critical thinking effectively.
By gathering and organizing relevant information, individuals can better grasp the context and background necessary for critical analysis.
Comprehension is the next step, building upon acquired knowledge. It involves the ability to understand and interpret information accurately, recognizing relationships between different ideas and concepts.
Comprehension allows individuals to go beyond superficial understanding and delve deeper into the underlying meanings and implications of the information they encounter.
Application is the practical utilization of knowledge and comprehension. It involves using acquired information and understanding to solve problems, make decisions, or tackle real-world situations.
Applying critical thinking skills means connecting theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios, finding relevant solutions, and considering potential consequences.
Analysis is the process of breaking down complex ideas or information into smaller parts to examine their components, relationships, and underlying structures.
It involves scrutinizing arguments, identifying biases, recognizing patterns, and discerning cause-and-effect relationships.
Analysis allows individuals to evaluate the validity, reliability, and relevance of information, enabling them to make well-informed judgments.
Synthesis involves combining different elements, perspectives, or ideas to create new insights, solutions, or understandings.
It requires integrating diverse information, concepts, or viewpoints into a coherent and meaningful whole.
Synthesis encourages individuals to think creatively, draw connections between seemingly unrelated concepts, and generate innovative solutions to complex problems.
Finally, evaluation is the critical assessment and judgment of ideas, arguments, or information based on specific criteria or standards.
It involves weighing evidence, considering different perspectives, and determining the credibility and quality of information.
Evaluation allows individuals to make reasoned judgments and decisions, considering the strengths, weaknesses, and potential biases inherent in the information or arguments they encounter.
Developing and honing critical thinking skills requires practice, reflection, and an open-minded approach.
It involves actively seeking out diverse viewpoints, questioning assumptions, considering alternative explanations, and being willing to revise one's own beliefs based on new evidence or insights.
By employing the six components of critical thinking—knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation, individuals can enhance their ability to think critically, make sound judgments, and navigate the complexities of the world around them.
. . . moving towards a more 21st Century #DirectDemocracy with Switzerland as a model
Swiss-style direct democracy, often referred to as "direct democracy with a federal council," is a unique form of governance that empowers citizens to participate directly in decision making processes at various levels of government.
Here's an overview of its key features, benefits, and considerations for adoption by other countries:
Key Features:
1. Referendums and Initiatives: Swiss citizens can propose changes to laws or the constitution through initiatives, and these proposals are put to a popular vote.
Referendums also allow citizens to challenge existing laws or government decisions.
2. Decentralized Governance: Switzerland is divided into cantons, each with substantial autonomy. This decentralization allows for regional variations in policies and a better representation of local needs.
3. Consensus Politics: Swiss politics emphasizes consensus-building and compromise. Decisions often require broad support to ensure stability and inclusivity.
Benefits:
1. Increased Civic Engagement: Swiss-style direct democracy encourages active citizen participation in political decision-making, fostering a sense of civic responsibility and engagement.
2. Responsive Government: It enables swift responses to emerging issues or public concerns, as citizens can trigger referendums or initiatives when they feel government actions are necessary.
3. Stability and Unity: The consensus-driven approach promotes political stability and helps bridge political divides by seeking common ground among diverse interest groups.
4. Regional Autonomy: Cantonal autonomy ensures that local issues are addressed effectively, promoting flexibility in governance.
Adoption Considerations:
1. Constitutional Framework: Adopting this system may require significant constitutional reforms, outlining the rules and procedures for referendums, initiatives, and decentralization.
2. Public Education: Implementing Swiss-style direct democracy requires educating citizens about their new roles and responsibilities in the decision-making process.
3. Balancing Representation: Striking a balance between direct democracy and representative democracy is crucial to prevent potential pitfalls such as populism or majoritarianism.
4. Cultural and Historical Context: Each country's unique political culture and history should be considered when evaluating the feasibility of adopting this system.
5. Size and Diversity: Smaller countries with manageable populations and diverse regions may find it easier to adopt Swiss-style direct democracy than larger, more homogenous nations.
While adopting Swiss-style direct democracy can enhance citizen participation and governance responsiveness, it's essential to tailor the system to each country's specific needs and circumstances.
It's not a one-size-fits-all solution, and careful planning and consideration are crucial for successful implementation.
The #DesignTeamProcess -- A Local Community Empowerment Tool
The great benefit of having a set of timeless, universal, and irreducible values and subsequent ethic and morality is that we can use them in analytical formats as the Design Team Process to design social processes, new social theories, and to test cultural, ethnic, racial, and gender assumptions, and existing social theories.
Several key elements are needed to produce the synergy of The Design Team Process: 1) The “Design Team” that is composed of 5-11 team members; 2) Specific roles of team members provide functions within the team to gather their collective intelligence during the inquiry process; 3) The “Social Sustainability Design and Validation Schematic” that guides their inquiry and can optionally be used as a “moral compass;” 4) The seven innate and universal values of Homo sapiens; and, 5) The subsequent ethic and morality of those values.
The Design Team Process provides a continuation of the traditional, long history of town hall meetings that uses a rational and synergistic process to gather the intelligence of small teams of local citizens to create solutions for common community, societal, and political problems.
The Design Team Process is fundamental for sustaining the legitimacy and effectiveness of the democratic process and the survival of democratic cultures.
Fortunately, the product of Local Community Design Teams can be shared with other Design Teams in democratic nations via the Internet to resolve ongoing social, political, and financial-economic problems and to resolve related issues.
The goal is to design socially sustainable social institutions that exist similarly in those nations, and to design organizations so that they, too, contribute to the social sustainability of those societies for the great benefit of all future generations.
#DanielRaphael PhD
>> PDF download
https://www.academia.edu/89261433/The_Design_Team_Process_A_Local_Community_Empowerment_Tool
. . . drafting a
#DirectDemocracyConstitution
We, the people

#ChatGPT
Constitution of [Country Name]
Preamble:
We, the people of [Country Name], establish this Constitution to secure our rights, promote our common welfare, and establish a system of government based on direct democracy. We believe that every citizen has the right to participate in decision-making and shape the destiny of our nation. We strive to create a just and inclusive society where the voice of every citizen is heard and respected.
Article I: #Sovereignty
Section 1: Popular Sovereignty
The ultimate authority and power of the government of [Country Name] reside in the people. All political power is derived from the people, and their right to participate in decision-making shall not be infringed.
Article II: Fundamental Rights
Section 1: Right to Equality
All citizens of [Country Name] are equal before the law. No discrimination shall be practiced on the basis of race, color, gender, religion, sexual orientation, nationality, or any other grounds.
Section 2: Right to Freedom of Speech and Expression
Every citizen has the right to freely express their opinions, thoughts, and beliefs, and to receive and impart information through any media of their choice.
Section 3: Right to Assembly and Association
Citizens have the right to peacefully assemble, protest, and form associations, including political parties, trade unions, and civil society organizations.
Section 4: Right to Vote and Participate in Decision-Making
Every citizen, regardless of age, gender, or any other criteria, has the right to vote and participate directly in the decision-making process of the government.
Article III: Direct Democracy
Section 1: Referendums
The people of [Country Name] have the right to propose, support, and vote on laws, policies, and constitutional amendments through referendums. A certain threshold of participation or majority shall be determined to validate the outcome.
Section 2: Citizen Initiatives
Citizens have the right to propose new laws or constitutional amendments through citizen initiatives. These proposals shall be subject to a thorough review process and, if supported by a significant number of citizens, be put to a referendum.
Section 3: Recall Elections
Citizens have the right to initiate recall elections to remove elected officials from office before the completion of their term. The recall process shall be determined by law.
Article IV: Government Structure
Section 1: Legislative Branch
The legislative branch shall consist of directly elected representatives who shall enact laws based on the will of the people. The legislative process shall be transparent and accessible to all citizens.
Section 2: Executive Branch
The executive branch shall be accountable to the people and act in accordance with their will. The head of state or government shall be elected directly by the citizens and serve as the representative of the people.
Section 3: Judicial Branch
The judicial branch shall ensure the independence and impartiality of the judiciary. Citizens shall have access to fair and timely judicial processes, and judicial decisions shall be subject to review.
Article V: Amendments
This Constitution may be amended through a direct democratic process. Proposed amendments shall be subject to public debate, and if supported by a majority of citizens, shall be implemented.
Article VI: Supremacy
This Constitution is the supreme law of [Country Name], and all laws, policies, and actions shall be in accordance with its principles. Any law or provision that contradicts the principles of this Constitution shall be considered null and void.
Conclusion:
This Constitution, based on the principles of direct democracy, is founded on the idea that the power and authority of the government derive from the people.
It ensures that all citizens have the right to participate in decision-making, and that their fundamental rights and freedoms are protected. By establishing this Constitution, we commit ourselves to building a society where equality, freedom, and justice prevail.
#DeliberativeDemocracy #Aristotle

The historical roots of deliberative democracy can be traced back to ancient Greek philosophers like Aristotle, who emphasized the importance of public discourse and debate in decision-making processes.
Aristotle believed that through deliberation, citizens could engage in reasoned and informed discussions, ultimately leading to better decisions for the community.
The first practical applications of deliberative democracy principles can be seen in the ancient Athenian democracy, where citizens would gather in the Ecclesia (assembly) to discuss and vote on important matters of state.
The concept of deliberative democracy gained renewed attention during the Enlightenment period, with thinkers like Jean-Jacques Rousseau and Immanuel Kant emphasizing the importance of public reason and collective decision-making.
Rousseau's concept of the "general will," which he believed could be formed through deliberation and consensus, was particularly influential.
In the modern era, deliberative democracy has been championed by political theorists like Jürgen Habermas and John Rawls.
Habermas's theory of communicative action and the "ideal speech situation" emphasized the importance of free and open discourse, where individuals could engage in rational and reasoned debate without coercion.
The development of deliberative democracy as a practical approach to decision-making has been influenced by various experiments and initiatives, such as citizens' juries, consensus conferences, and deliberative polling.
These methods aim to create structured environments where diverse groups of citizens can engage in informed and facilitated discussions on complex issues, with the goal of reaching well-reasoned and consensus-based decisions.
In recent decades, deliberative democracy has been adopted in various forms by governments and organizations around the world.
For example, participatory budgeting, where citizens directly deliberate on the allocation of public funds, has been implemented in numerous cities worldwide.
Additionally, many countries have established citizens' assemblies or conventions to deliberate on constitutional reforms or other significant policy issues.
Overall, the historical roots of deliberative democracy can be traced back to ancient philosophical concepts.
Its practical applications and further development have been shaped by modern political theory and the desire to create more inclusive and participatory forms of decision-making.
#Democracy #Sustainability
A democratic society will only become sustainable when the combined decisions and actions of individuals and organizations work for the same goals of sustainability.
Both have an equal moral responsibility for the survival and sustainability of future generations.
Both are required to maintain the continuity of society by preventing social disintegration and ensuring that a democratic society evolves.
Only then will society be able to provide an improving quality of life and the potential of growth equally for everyone, and assure the same for future generations.
Dave, you still chatting with plebs?
Hey Dave, what do you know about the history of Distributive Democracy. Where it began, examples of how it was used and developed. Where and how it is being used today.
#DeliberativeDemocracy #Dialogue
From #Governance to #Healthcare to #Education Reform to a National #Energy Policy to #Taxation
Imagine small groups of citizens coming together. Meeting in a facilitated conversation.
Where everyone has a chance to share their perspective on a community, town, city, state, province, territory, prefecture or national issue.
And participate in re-imagining and design.
This is the essence of Deliberative Democracy in action.
#Community #Engagement

Deliberative Democracy in the Age of #Bitcoin
The 21st century presents a unique landscape for democratic participation.
Traditional representative democracy, where citizens elect officials to make decisions on their behalf, faces increasing scrutiny in an age of growing distrust and social division.
However, a potential path forward lies in the resurgence of #deliberativedemocracy, an approach that emphasizes reasoned discussion and citizen engagement in shaping public policy.
This concept takes on even greater intrigue when viewed through the lens of the
#BitcoinStandard.
Deliberative democracy goes beyond simply casting a vote.
It envisions a process where citizens actively participate in discussions about important issues, exchanging ideas, and ultimately arriving at decisions through a well-informed exchange of perspectives.
This focus on deliberation, rather than solely on voting, is the heart of this democratic ideal.
In the context of the Bitcoin Standard, as outlined in Saifedean Ammous' influential book, deliberative democracy offers a framework for citizens to potentially reshape the very foundation of economic decision-making.
Core Principles Reimagined
Deliberation in a Digital Age
The core principles of deliberative democracy remain vital in the 21st century, but the rise of the Bitcoin Standard necessitates a nuanced reimagining of how these principles are applied.
Reasoned Discussion with a Global Scope
Discussions in deliberative processes traditionally focused on national or regional issues.
The borderless nature of Bitcoin necessitates a broader perspective.
Citizens from across the globe could potentially participate in discussions about the future of digital currencies, ensuring diverse viewpoints are considered when shaping regulations or potential adaptations to the Bitcoin Standard.
Equality of Participation and Access to Information
The decentralized nature of Bitcoin emphasizes transparency and accessibility.
Deliberative processes in this context should strive for the same level of inclusivity.
This could involve utilizing online platforms to facilitate discussions, ensuring citizens from all walks of life have access to the information and resources needed to participate meaningfully.
Reciprocity and Finding Common Ground in a Decentralized World
The absence of a central authority in a Bitcoin Standard system necessitates a strong sense of shared purpose and collective responsibility among citizens.
Deliberative processes can foster this by encouraging participants to approach discussions with an open mind, willing to consider alternative perspectives and work towards solutions that benefit the global community.
Informed Citizenry with Financial Literacy
Understanding the intricacies of a Bitcoin Standard system is crucial for informed participation in deliberative processes.
Educational initiatives could be incorporated into these processes, equipping citizens with the financial literacy necessary to engage in meaningful discussions about the economic implications of this new monetary paradigm.
Models and Methods of Deliberation in a Decentralized Future
The rise of the Bitcoin Standard opens doors for innovative models and methods of deliberation.
Here are a few possibilities:
Global Citizens' Assemblies
Leveraging video conferencing and online platforms, geographically dispersed citizens could be randomly selected to participate in extended discussions about the future of a Bitcoin Standard system.
These assemblies could focus on specific issues like regulatory frameworks or potential adaptations to the economic model.
Blockchain-based Deliberation Platforms
Blockchain technology, the foundation of Bitcoin, could be used to create secure and transparent online platforms for deliberation.
These platforms could facilitate discussions, voting on proposals, and ultimately recording the outcomes of these deliberative processes on a tamper-proof public ledger.
Liquid Democracy with Micropayments
The concept of liquid democracy, where citizens can delegate their voting power to trusted individuals, could be adapted to a Bitcoin Standard system.
Micropayments facilitated by the Bitcoin network could incentivize participation and ensure delegated votes are used responsibly.
These models are just a glimpse into the possibilities that a Bitcoin Standard could unlock for deliberative democracy.
The key lies in harnessing the power of technology to create inclusive, transparent, and secure platforms for citizen engagement.
A New Frontier for Democratic Participation
Deliberative democracy in a Bitcoin Standard system offers several potential benefits:
More Informed Economic Decisions
Through reasoned discussion, citizens can gain a deeper understanding of complex issues surrounding decentralized currencies, potentially leading to more informed and nuanced economic policies.
Increased Legitimacy for a Decentralized System
When citizens feel their voices are heard and considered in shaping the rules governing a Bitcoin Standard system, it fosters trust and acceptance of this decentralized economic model.
Reduced Polarization Around Economic Issues
Open and respectful deliberation can encourage empathy and understanding of diverse economic viewpoints, potentially mitigating societal divisions that often arise from traditional fiat currency systems.
Empowering Citizens in a Decentralized World
Active participation in deliberative processes around the Bitcoin Standard can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility among citizens for the health and stability of the global economy.
However, there are also challenges to consider.
Digital Divide
Not everyone has equal access to the technology and internet connectivity needed to participate in online deliberative processes.
Efforts to bridge the digital divide will be crucial to ensure equitable participation in a Bitcoin Standard system.
Security Concerns
Online platforms for deliberation need robust security measures to protect against hacking and manipulation.
The decentralized nature of the Bitcoin network offers some inherent security advantages, but ensuring the integrity of these platforms will remain a critical concern.
Scalability and Representation
Deliberative processes with a global scope present challenges in terms of scalability and ensuring truly representative participation.
Finding the right balance between inclusivity and manageable group sizes will be crucial.
Navigating Complexities
The world of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology is complex.
Equipping citizens with the necessary financial literacy to participate meaningfully in deliberations remains a significant hurdle.
A Deliberative Future for a Decentralized World
The Bitcoin Standard presents a unique opportunity to reimagine democratic participation in the 21st century.
Deliberative democracy, with its emphasis on reasoned discussion and citizen engagement, offers a framework for navigating the complexities of a decentralized economy.
By embracing innovative models, harnessing the power of technology, and addressing the challenges head-on, we can create a deliberative future.
Where citizens actively shape the rules and regulations governing a Bitcoin Standard system, fostering a more informed, inclusive, and ultimately, a more prosperous future for all.
