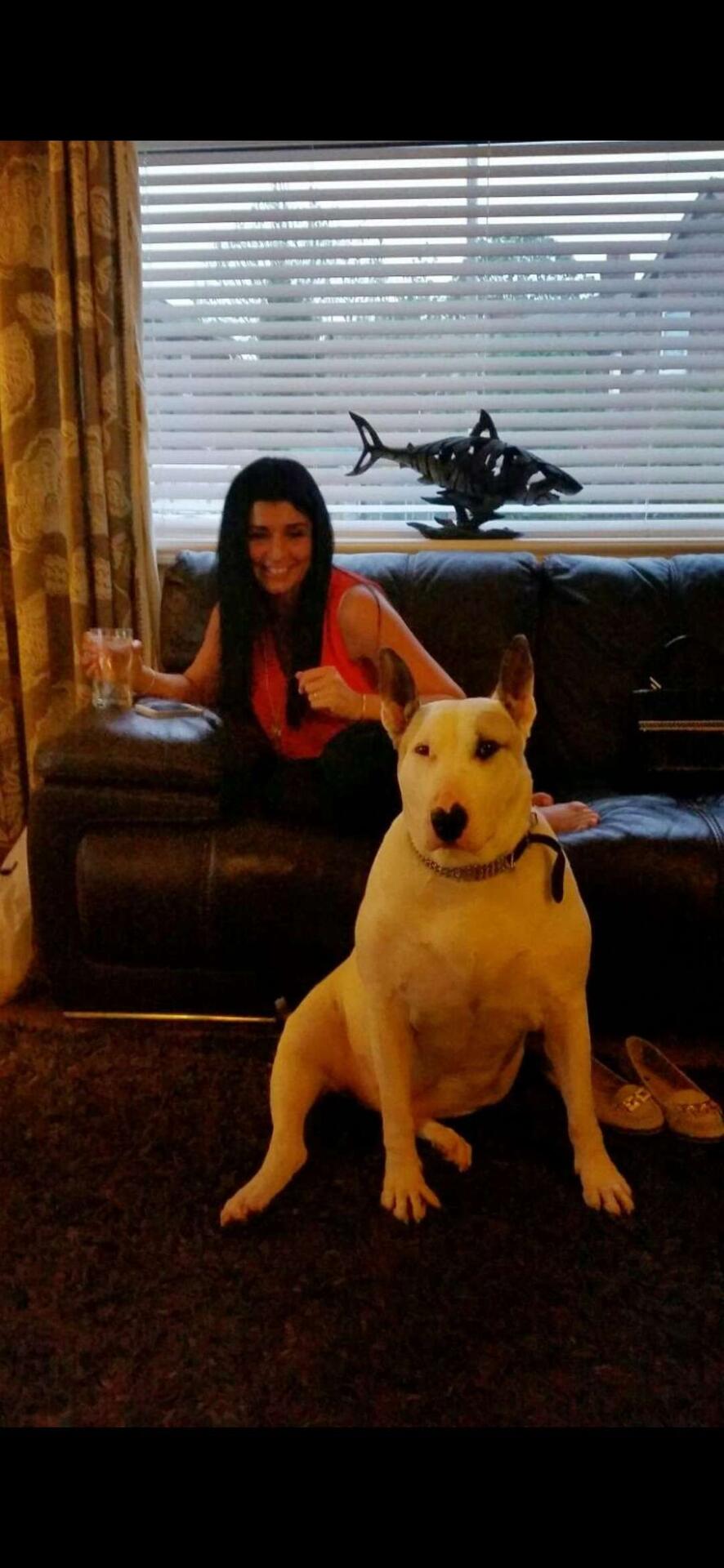
The dog’s nose truly resembles a heart. It’s as if he’s smelling the world with his heart. RIP🫡
The brain is truly fascinating. During the day, when we recall the past, it tends to highlight our pleasant memories, filling us with a sense of peace. Yet, as soon as we lie down to sleep, it brings forth our most embarrassing memories, robbing us of sleep. It’s almost as if the brain’s existence is like a form of natural schizophrenia.
This duality can be explained from an evolutionary perspective. Our brain has a tendency to suppress negative memories over time and emphasize positive ones, a phenomenon known as “positive illusion.” This mechanism might have evolved to protect our mental well-being and to maintain our motivation for survival. Constantly dwelling on traumatic or negative events could lead to chronic stress, which would lower our chances of survival. By highlighting the positive, the brain helps us stay resilient, and this sense of nostalgia is further reinforced by the release of hormones such as serotonin and oxytocin, which enhance feelings of warmth and tranquility.
On the other hand, the brain’s tendency to bring up shameful memories just before sleep can also be traced back to evolutionary functions. The moments before sleep involve a shift to alpha and theta brainwave states, where our connection with the subconscious becomes more pronounced. The brain might be presenting these memories to process them, ensuring that we don’t repeat socially risky behaviors in the future. Especially before important days or in moments of stress, this might serve as a preparatory process, allowing us to learn from past mistakes.
Additionally, since moments before sleep or before an important day tend to be more anxiety-inducing, the brain’s focus on past embarrassing events could be an attempt to rehearse avoiding similar situations, even though in modern life this mechanism often becomes counterproductive…
Sometimes going back to old songs feels like a nostalgic therapy
It's really great to see such developments. As stubborn as the 'big brothers' are, we continue to evolve just as much.
Also, I've learned through this occasion that Tutanota has changed its name to Tuta :D thanks
What is Post-Quantum Cryptography and Why is it Important?
Post-quantum cryptography refers to encryption techniques designed to be secure even against the power of quantum computers. Current encryption methods such as RSA, DSA, and ECC rely on mathematical problems that are practically impossible for classical computers to solve. However, quantum computers have the potential to break these codes quickly. As a result, post-quantum cryptography focuses on using mathematical problems that even quantum computers find incredibly difficult to solve.
Alice and Bob’s Post-Quantum Security Adventure
To illustrate, let’s revisit our classic characters, Alice and Bob. Alice wants to send a secure message to Bob, but she knows that there’s a risk of Eve, a malicious eavesdropper equipped with a quantum computer, intercepting the message. Alice needs to use post-quantum encryption techniques to ensure her communication remains secure.
1. Lattice-Based Cryptography
- Scenario: Alice decides to use lattice-based cryptography to send a post-quantum secure message to Bob.
- How It Works: In lattice-based cryptography, Alice represents her message as a point within a large, multi-dimensional grid (lattice). She then sends Bob a "short vector" that helps him locate the correct point within this grid, allowing him to decode the message.
- Alice’s Steps:
1. Constructs a large, multi-dimensional lattice and encodes her message as a point within this grid.
2. Encrypts this point with a special key and sends it, along with a "short vector," to Bob.
- Bob’s Steps:
1. Uses the short vector and the key to navigate the lattice and find Alice’s original message.
- Eve’s Challenge: Even with a quantum computer, Eve faces an overwhelming mathematical challenge to decode the message. The complexity of the lattice makes it virtually impossible to determine the correct point without the proper vector and key.
2. Code-Based Cryptography
- Scenario: Alice and Bob use a code-based encryption technique to communicate.
- How It Works: Alice encodes her message using a random error-correcting code and sends it to Bob. While Bob has the necessary key to correct these errors, Eve cannot decipher the message without it.
- Alice’s Steps:
1. Takes her message and encodes it with random errors using a code-based encryption technique.
2. Sends the encoded message to Bob.
- Bob’s Steps:
1. Uses his secret decoding key to correct the errors and extract Alice’s original message.
- Eve’s Challenge: Without the error-correction key, Eve faces an insurmountable task in decoding Alice’s message, even with a quantum computer.
3. Hash-Based Signatures
- Scenario: Alice needs to send a digitally signed message to Bob to ensure its authenticity.
- How It Works: Alice generates a hash (a condensed representation) of her message and then uses her private key to create a digital signature. This signature, along with the original message, is sent to Bob, who can verify its authenticity using Alice's public key.
- Alice’s Steps:
1. Creates a hash of her message.
2. Signs the hash using her private key and sends both the message and the signature to Bob.
- Bob’s Steps:
1. Uses Alice’s public key to verify that the signature matches the hash, ensuring the message’s authenticity.
- Eve’s Challenge: The hash function is designed to be computationally infeasible to reverse, even for quantum computers, meaning Eve cannot forge Alice’s signature or tamper with the message.
Quantum Computers’ Cracking Abilities: Shor and Grover Algorithms
- Shor’s Algorithm: This quantum algorithm efficiently factors large numbers, which would compromise RSA and ECC encryption methods.
- Grover’s Algorithm: It accelerates the search process for finding pre-images of hash functions, but post-quantum cryptographic methods are constructed to withstand even this enhanced capability.
Hybrid Encryption: A Practical Approach
In practical applications, Alice and Bob may use a combination of post-quantum algorithms alongside traditional encryption methods to maximize security:
- Alice uses a post-quantum algorithm to encrypt a shared secret key.
- She then uses a classical encryption method, like AES, to encrypt the actual message using that key.
This hybrid approach provides protection against both current classical threats and future quantum threats.
The Real-World Importance and Applications of Post-Quantum Cryptography
Post-quantum cryptography is not just a theoretical concept; it has started to be implemented in various applications* . From financial transactions to secure communication, integrating post-quantum algorithms into existing systems offers early protection against the emerging quantum threat. This shift is essential to safeguard data against the possibility of future quantum attacks.
Conclusion
Post-quantum cryptography represents a critical advancement in safeguarding data against the potential dangers posed by quantum computers. Lattice-based, code-based, and hash-based encryption techniques provide layers of security that are designed to withstand even the most advanced quantum attacks. Through Alice and Bob’s journey, we've explored how these post-quantum algorithms function and why they are so vital for future-proofing our digital security.
As the capabilities of quantum computers continue to grow, the adoption of post-quantum cryptographic techniques will be an essential step in ensuring that our information remains protected. This isn't just a temporary fix but a foundational element in securing a future where quantum threats are a reality.
* For example: mullvad vpn, which I love to use, uses these algorithms practically. Not advertising
#privacy #cryptography #freeinternet #nostr #edu #postquantum #xmr #monero #btc #bitcoin
Who knows what the future holds, but being here gives me a sense of inner fulfillment that makes me feel I’m in the right place…
These streaming platforms’ subscription systems have gone to shit
On Nostr, there are now replyguys who respond even to the replies of other replyguys🤦🏼♂️ I wonder if these people have a rational reason for their existence that I’m unaware of
#nostr #asknostr
One bitcoin is worth 588 dollars :,) I hope he listened to this advice…
:,) #meme #memes #love

Trying to kill your ego is simply acknowledging its existence. As Lao Tzu said, ‘He who knows others is wise; he who knows himself is enlightened.’
Temet Nosce🫡
Similarities Between Religions and Blockchains
When we consider the similarities between religions and blockchains, it’s fascinating to discover how they share some intriguing commonalities.
First of all, both systems revolve around a “type of book.” Religions center around sacred texts, while blockchains create their own “ledgers” (blockchain records). Religious teachings are often found in holy books, and although these books may have been written at different times, they essentially contain compatible messages. Similarly, blockchains maintain records in each block, which are linked over time to form a chain. Both aim for a sense of continuity and coherence.
Throughout history, religions have given rise to many versions, with some “forking” the original texts to create new interpretations🤣. In the same way, blockchains evolve through various “forks.” A group of developers might take an existing blockchain and create a new version. This is like a group of devoted followers creating a “new commentary” on an old religion.
#btc #bitcoin #nostr #religion #blockchain #meme #memes
Haha, holy privacy. I just realized that religions are somewhat similar to blockchains. Everyone has many copies of religious texts, and some groups create their own versions of religious texts and ‘fork’ their religion🤣
In Nostr, the ease of increasing follower count (as easy as writing a software bot) makes it gradually lose its significance. The self-censorship that follower counts induce on traditional social media disappears here. This enables us to use social media more freely. Simplicity can sometimes lead to insignificance, but this insignificance can liberate us. It creates a space where we can share our thoughts without being concerned about follower numbers.
#nostr #grownostr #damus
I really love Australia, and a part of me always wants to live there—probably because of the desire to escape from the world's current events :D. Anyway, the strangeness of the animals in Australia both makes me uneasy and piques my interest. I think one of the reasons for the animals growing larger in Australia is an ecological process called island gigantism, which is also studied in the theory of evolution. It’s a fun topic worth researching 👍🏻
How Are Atomic Swaps Secure Even Though They Are Off-Chain?
On-Chain vs. Off-Chain Swaps:
Atomic swaps can occur both on-chain and off-chain. Off-chain swaps happen outside the main blockchain, which speeds up transactions and reduces the load on the network. However, the primary concern is how to ensure security in off-chain transactions. Off-chain atomic swaps are often executed through second-layer solutions like the Lightning Network.
In off-chain swaps, security is primarily maintained using Hashed Time-Locked Contracts (HTLCs) and cryptographic verifications. HTLCs are crucial in both on-chain and off-chain atomic swaps.
Technical Details:
What Are HTLCs?
HTLCs are smart contracts that impose conditions based on time and cryptographic hash values. They ensure that a transaction will only complete if a specific encrypted value (hash) is revealed within a set time frame. If the value is not revealed, the transaction is canceled, and the funds are returned. These two mechanisms maintain security.
uploaded as image HTLC code example
What’s Happening Here?
1. Contract Creation: Alice initiates the contract to swap with Bob. Alice creates a hash value (hashlock), and Bob needs to unlock it by providing the preimage. There is also a time limit (timelock) defined; if the swap is not completed in time, Alice can retrieve her funds.
2. Withdraw Function: Bob unlocks Alice’s funds by providing the correct preimage. The contract checks whether the preimage matches the hashed value using keccak256 hashing.
3. Refund Function: If Bob fails to provide the preimage within the time limit, Alice can call the refund function to retrieve her funds.
The security of this system relies on the cryptographic hash lock and the time-bound conditions. Both parties must act within the time constraints and with the correct information, or the funds will be refunded, ensuring no loss of assets.
Additional Security in Off-Chain Atomic Swaps:
In off-chain atomic swaps, additional security is ensured through second-layer solutions like the Lightning Network. Transactions happen outside the main blockchain and are finalized without being recorded on-chain. Security is ensured using multi-signature wallets and signed data that validate every step of the process.
Example: When Alice and Bob perform an atomic swap through the Lightning Network, they open payment channels. These channels ensure that funds cannot be moved without both parties’ signatures. In case of a dispute, the payment channels are closed, and the funds revert to the main blockchain, guaranteeing security.
#btc #bitcoin #xmr #monero #eth #ethereum #evm #contract #solidity #code #atomic #swap #edu 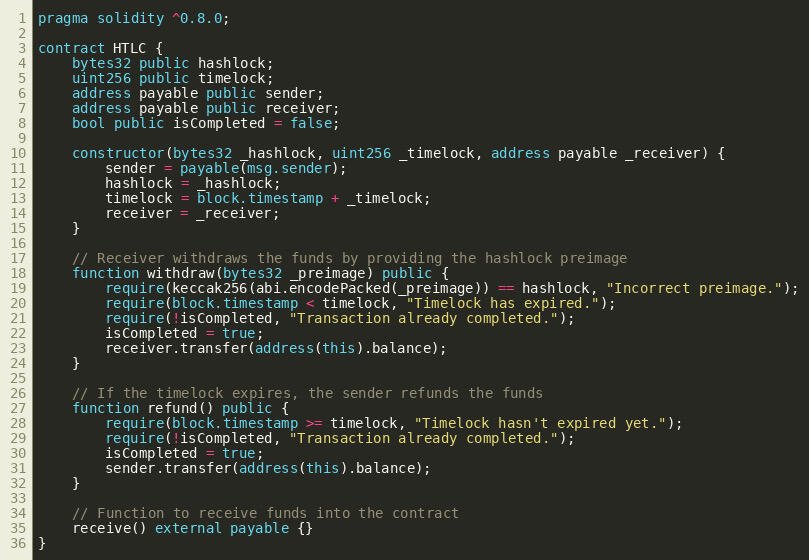
Cross-Chain Atomic Swaps in Bitcoin: How Do They Work?
Bitcoin is a decentralized and secure digital currency that allows users to exchange value without relying on a central authority. However, transferring assets between different blockchains (for example, Bitcoin and Ethereum) can be challenging because these systems are not inherently designed to interact with each other. This is where cross-chain atomic swaps come into play. This technology enables the exchange of cryptocurrencies between two different blockchains without the need for a third-party intermediary. So, how does it work?
Atomic swaps allow two parties to exchange digital assets on different blockchains without relying on each other’s trust or a centralized middleman. The term “atomic” refers to the fact that the transaction either happens fully or doesn’t happen at all. Both parties either get what they want or the deal is canceled, leaving everyone with their original assets.
To understand this better, let’s use the classic “Alice and Bob” example. Alice has Bitcoin, and Bob has Ethereum. Alice wants to exchange her Bitcoin for Bob’s Ethereum, and Bob wants to exchange his Ethereum for Alice’s Bitcoin. However, they don’t trust each other, so they decide to use a cross-chain atomic swap instead of going through a centralized exchange.
Step 1: Alice Locks Her Bitcoin
Alice creates a contract on the Bitcoin blockchain using a Hashed Time-Locked Contract (HTLC). This contract locks her Bitcoin for a certain period of time and can only be unlocked by Bob if he knows a specific “secret” that Alice has generated (the hash of the secret is used in the contract).
Step 2: Bob Locks His Ethereum
Bob also creates an HTLC on the Ethereum blockchain, locking his Ethereum. This contract allows Alice to claim Bob’s Ethereum, but only if Alice reveals the secret used to unlock her Bitcoin. Bob can’t unlock Alice’s Bitcoin without this secret, and Alice can’t unlock Bob’s Ethereum without revealing it.
Step 3: Alice Claims Bob’s Ethereum
Alice now uses the secret to unlock Bob’s Ethereum. This action is recorded on the Ethereum blockchain, and Bob can see that Alice has revealed the secret.
Step 4: Bob Uses the Secret to Claim Alice’s Bitcoin
Bob, having seen the secret that Alice used, now uses it to unlock Alice’s Bitcoin. Thus, both parties successfully complete the swap without ever needing to trust each other or involve a third party.
If at any point the swap isn’t completed (for example, if one party doesn’t unlock their assets within the time limit), the contracts will automatically expire, and the funds will be returned to their respective owners. This ensures the system remains safe and fair.
Why Use Atomic Swaps?
• Security: No need for a centralized exchange or a trusted third party.
• Privacy: More private than conducting trades on an exchange.
• Decentralized: No one can stop or delay the transaction
#btc #bitcoin #eth #ethereum #xmr #monero #nostr #edu #atomic #swap