i was looking at this same article the other day, been thinking about it...
Discussion
hugging face always has good blog posts too https://huggingface.co/blog/embedding-quantization#retrieval-speed
Looks simple enough. I imagine you could even go further with a sparse encoding scheme assuming there are huge gaps of 0 bits, which is probably the case for high dimensional embeddings. 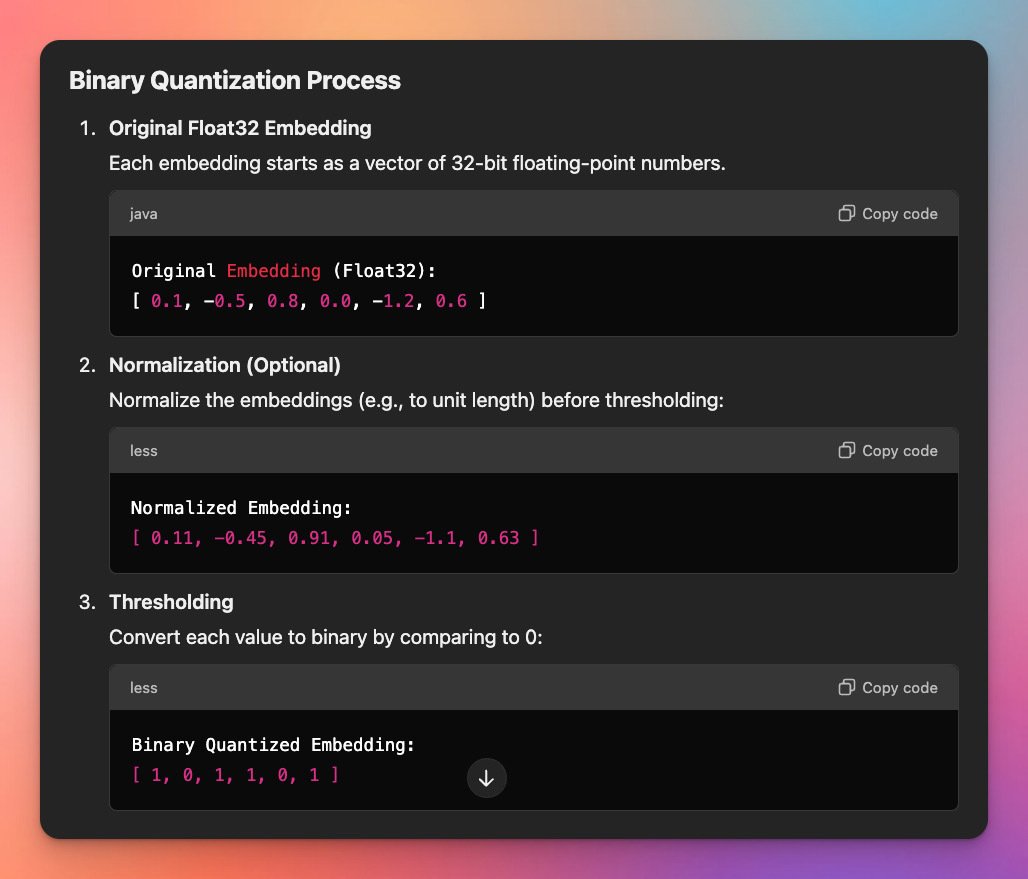
curious if it’s being used anywhere yet
I hear my laptop's fans start whirring around when its making a response, I wouldn't be surprised if its doing something locally first. Either the encoding process (words to tokens) or the retrieval (finding relevant documents from a project)
retrieval maybe?
btw have you seen https://www.mixedbread.ai/blog/mxbai-embed-large-v1
wait nvm encoding should be first no? Since converting words to tokens is usually needed before retrieval unless the retrieval uses pre-computed embedding, maybe it skips straight to that? Idk
Think of how you 'hold a memory', no one else can interact with it unless you talk about it or draw it, a memory or idea needs to be conveyed somehow to the outside world. An encoding models that produce embeddings are basically half an LLM, it takes in the words/tokens and says "this string is located here", it assigns a coordinate, an address for it. That address is the context, anything with addresses nearby are more related in ideas. The second part of the LLM is the decoder, where it takes the address as a kind of starting point. The decoder uses the context of that coordinate and responds with words that are also in the right context (which is learned by training).
H.T. to nostr:npub1h8nk2346qezka5cpm8jjh3yl5j88pf4ly2ptu7s6uu55wcfqy0wq36rpev for his fantastic read of "A gentle introduction to Large Large Language Models"


