Seems easy to fool 10 people than 100000 🫡🫡
All chefs posting the reply here.
Why #nostur load the new post when I am reading one. It doesn’t stop. Seems a stupid design or I am lost in settings. #asknostr
#notedeck 
where are my decks on ubuntu, which i created on my macbook, same keys. still synching yet
banger note here, bit tricky to install and to open on Ubuntu 24.04. But works like charm. hmmm webm not a valid file to upload yet. after installation have to use cmd line to check if installed or not and then cmd to open it as well
lets take screen shot of webm. it might me my pc need reboot.!!!! 
Key principles for using Bayesian thinking:
1. **Start with base rates**: Always consider how common something is in general
2. **Weigh evidence quality**: Strong evidence should change beliefs more than weak evidence
3. **Update gradually**: Change beliefs in steps as new information comes in
4. **Avoid extremes**: Be cautious about 0% or 100% certainty
5. **Consider alternative explanations**: Look for other possibilities. nostr:npub1sg6plzptd64u62a878hep2kev88swjh3tw00gjsfl8f237lmu63q0uf63m
Apparently nostr:npub1sg6plzptd64u62a878hep2kev88swjh3tw00gjsfl8f237lmu63q0uf63m was invited to give a talk at FOSDEM and lots of people got upset about it. I have no idea if the talk will happen, but I do wonder if these guys protesting understand that the vast majority of open source projects are sponsored and funded by corporations. To not include and understand the motivations of those companies and how they use and support open source feels like willful ignorance.
The first freedom of free software is that you can run the code for any purpose, including as a business making money it capitalism.
Bayes' Theorem and show how it applies to everyday decision-making and belief updating.
Let me explain how Bayes' Theorem helps us think better in everyday life:
1. **Starting Point (Prior)**: Begin with your initial belief about something. For example:
- "I think there's a 50% chance it will rain tomorrow"
- "I believe there's a 30% chance this restaurant is good"
2. **New Evidence**: You get new information that could change your belief:
- Weather: You see dark clouds gathering
- Restaurant: You see many positive reviews
3. **Update Your Belief**: Bayes' Theorem helps you rationally update your initial belief based on the new evidence.
Real-life examples:
1. **Job Interview**
- Prior: 40% chance of getting the job (based on typical odds)
- Evidence: Interview went very well
- Update: Increase your estimate to perhaps 60-70%
2. **Medical Diagnosis**
- Prior: 1% chance of having a condition (population average)
- Evidence: Positive test result (80% accurate)
- Update: New probability considering both pieces of information
3. **Relationship Red Flags**
- Prior: 80% chance relationship is healthy
- Evidence: Partner shows concerning behavior
- Update: Revise assessment based on new information
Key principles for using Bayesian thinking:
1. **Start with base rates**: Always consider how common something is in general
2. **Weigh evidence quality**: Strong evidence should change beliefs more than weak evidence
3. **Update gradually**: Change beliefs in steps as new information comes in
4. **Avoid extremes**: Be cautious about 0% or 100% certainty
5. **Consider alternative explanations**: Look for other possibilities
I am too lazy to do post stretch exercises but you said so will start over again.
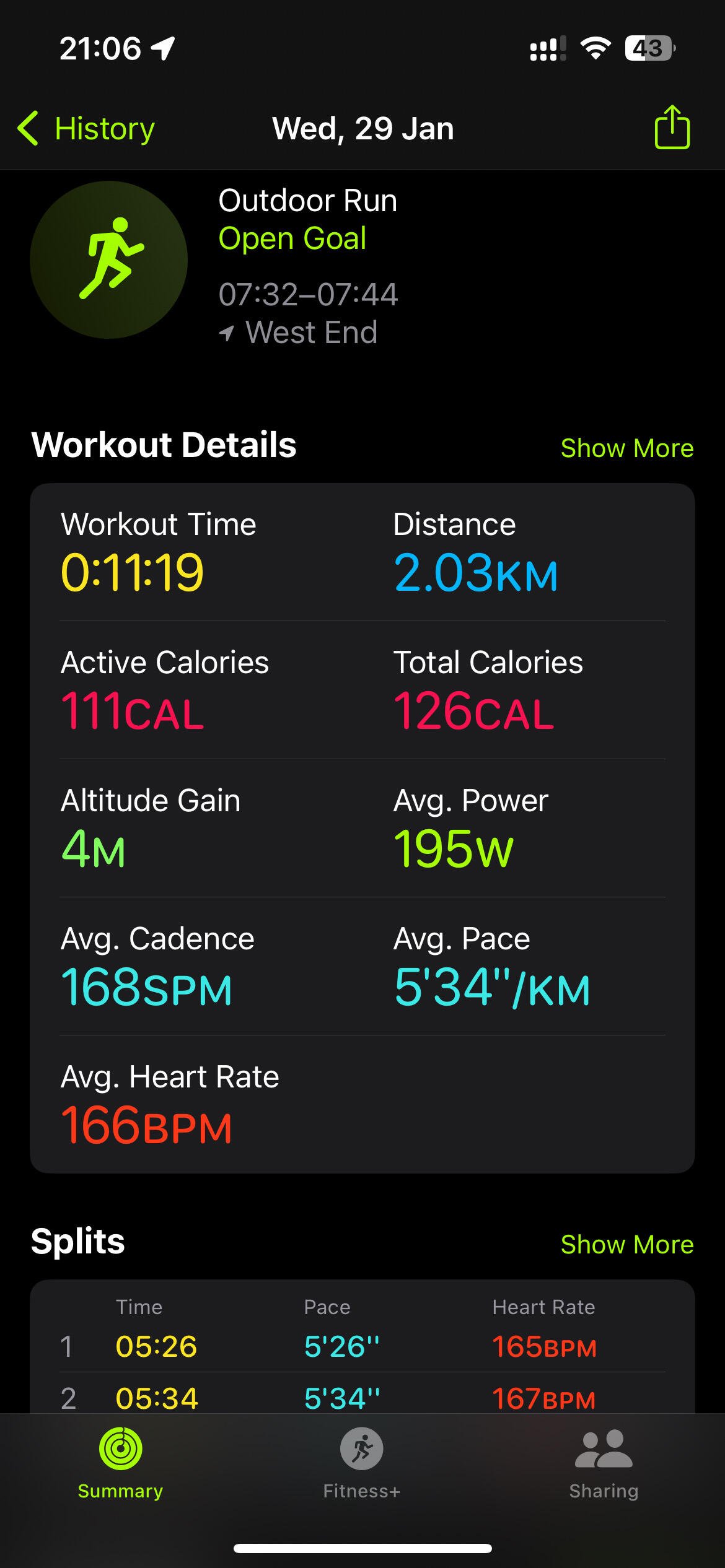
Yeh averaging around 20k a week , but resting for last 11 days due calf & hamstring spasms
I don’t have a much experience, but looks like they have a better privacy than standard virtual private network nostr:npub188x98j0r7l2fszeph6j7hj99h8xl07n989pskk5zd69d2fcksetq5mgcqf